Basics of Communication
Meaning and Significance of Communication
Communication is an essential part of our lives. It is the process through which we share ideas, information, and emotions with others. Whether it is a casual conversation with friends, a business meeting, or a lecture in a classroom, communication plays a crucial role. It helps in building relationships, sharing knowledge and solving problems. Effective communication is important for personal, academic, and professional success. It allows us to express our thoughts clearly and understand others better. Communication is not just about speaking or writing; it also includes listening, observing, and interpreting non-verbal cues. In today’s interconnected world, the ability to communicate effectively is more important than ever. It helps us connect with people from different cultures and backgrounds, fostering understanding and collaboration. Thus, understanding the meaning and significance of communication is vital for everyone.
Communication is the foundation of all human interaction. We would struggle to express our needs, share our thoughts, or build relationships without it. From the simplest daily interactions to complex negotiations, communication is the tool that enables us to navigate our social world. For example, when you greet someone, ask for directions, or explain a concept, you are engaging in communication. Each interaction, no matter how insignificant it may seem, contributes to the building of relationships and the sharing of knowledge.
Communication skills are highly valued in the professional world. Employers look for individuals who can articulate their ideas clearly, work well in teams, and interact positively with clients and colleagues. Good communication can lead to better job performance, career advancement, and improved workplace relationships. It enables individuals to negotiate, persuade, and resolve conflicts effectively.
In our personal lives, communication is the foundation of healthy relationships. It allows us to express our feelings, resolve conflicts, and build trust with family and friends. Good communication fosters understanding and empathy, which are essential for maintaining strong and meaningful connections.
Definitions of Communication
- Communication is the act of transferring information from one place, person, or group to another.
- Communication is a process by which information is exchanged between individuals through a common system of symbols, signs, or behaviour.
- Communication is a two-way process of reaching mutual understanding, in which participants not only exchange information but also create and share meaning.
Communication is a fundamental human activity that involves the exchange of information, ideas, and feelings. It can occur through various means such as speech, writing, gestures, and visual aids. Effective communication requires both a sender and a receiver, and it involves not just the transmission of messages but also the interpretation and understanding of those messages. Good communication skills are essential in every aspect of life, from personal relationships to professional settings. They help in expressing thoughts clearly, building relationships, and resolving conflicts. Understanding the different aspects and processes of communication can significantly enhance one’s ability to communicate effectively. Effective communication is more than just conveying a message; it involves ensuring that the message is understood as intended.
Process of Communication
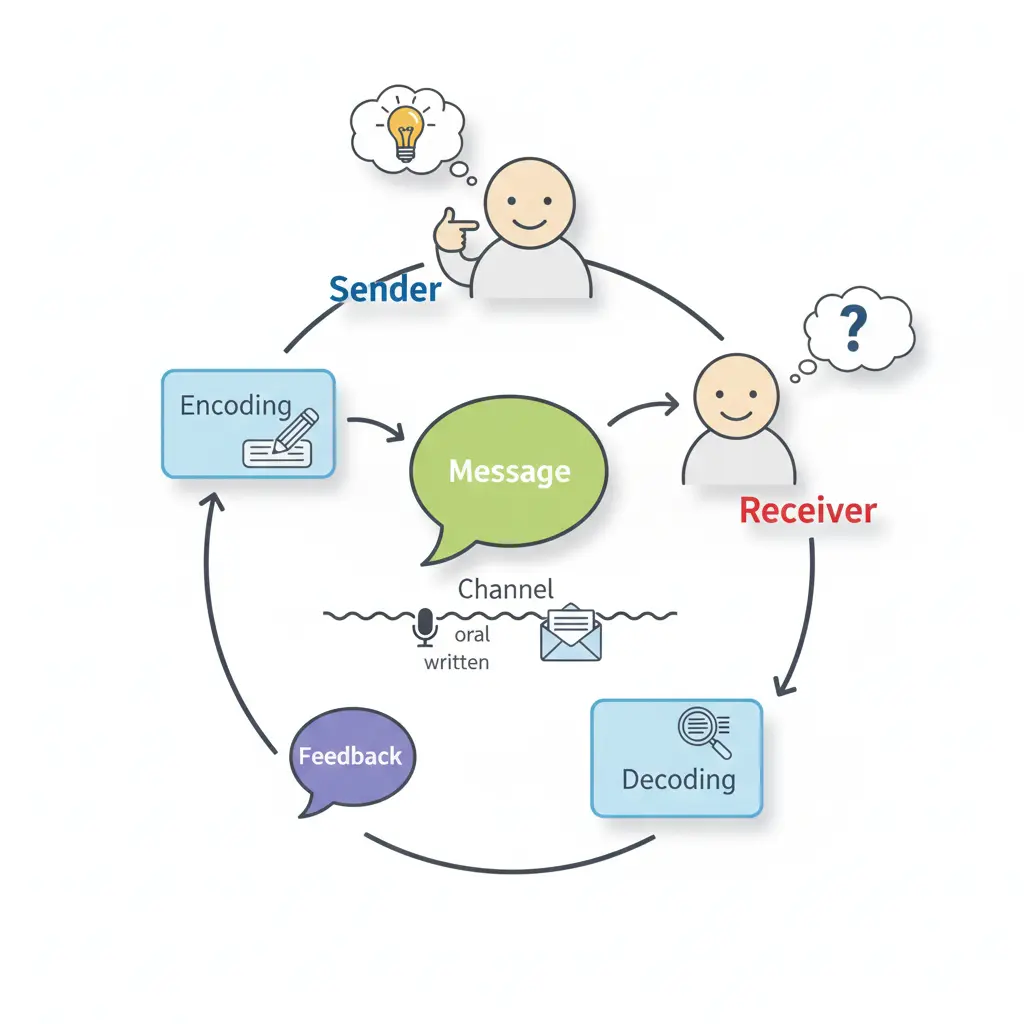
The process of communication is the series of steps that allow the transfer of information from one person to another. It involves several components that work together to ensure that the message is delivered and understood correctly. Understanding the communication process is crucial for effective interaction, as it helps to identify potential barriers and improve the clarity of the message. In this section, we will explore the components of the communication process and how they function together.
The communication process is a cyclical process that begins with the sender and ends with feedback from the receiver. Each component in this process plays a vital role in ensuring that the message is clear and understood as intended. The process can be disrupted at any stage by barriers such as noise, misunderstanding, or lack of clarity. Therefore, understanding each component and its role in the communication process is essential for effective communication.
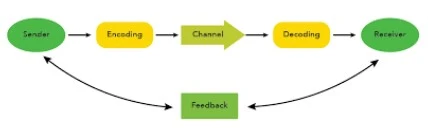
Components of Communication
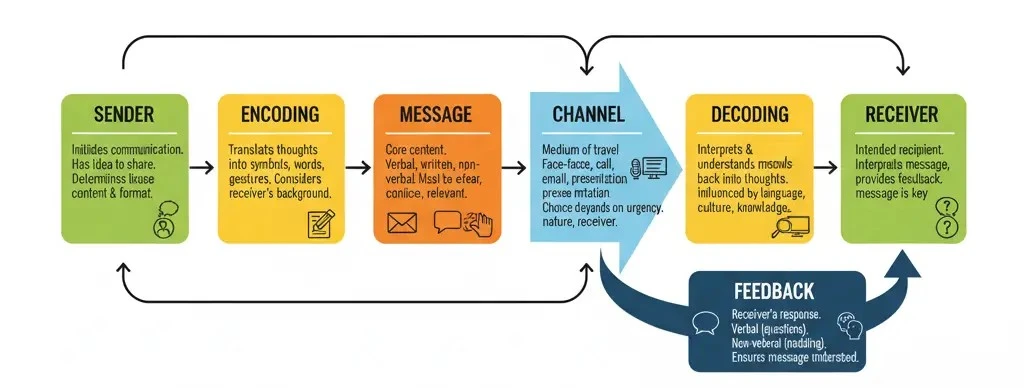
Sender: Sender is the person who initiates the communication. The sender has an idea or information that they want to share. The sender’s role is crucial because they determine the content and format of the message. The effectiveness of communication largely depends on the sender’s ability to encode the message clearly and appropriately.
Encoding: Encoding involves translating the sender’s thoughts and ideas into symbols, words, or gestures that the receiver can understand. This process requires careful consideration of the receiver’s background, knowledge, and context to ensure that the message is clear and meaningful.
Message: The message is the core content of the communication. The message can be verbal, written, or non-verbal, and it must be clear and concise to avoid confusion. The clarity and relevance of the message are critical for effective communication. Using clear and simple language, avoiding jargon, and providing examples can help make the message more understandable.
Channel: The channel is the medium through which the message travels from the sender to the receiver. It can be a face-to-face conversation, a phone call, an email, or a visual presentation. Choosing the appropriate channel is essential for effective communication, as different channels have different strengths and limitations. For example, face-to-face communication allows for immediate feedback and non-verbal cues, while written communication provides a permanent record. The choice of channel depends on various factors, including the nature of the message, the urgency, and the preferences of the receiver.
Decoding: Decoding is the process of interpreting and understanding the encoded message. The receiver translates the symbols, words, or gestures back into thoughts and ideas. Effective decoding depends on the receiver’s ability to understand the message as intended by the sender. Factors such as language proficiency, cultural background, and prior knowledge can influence the decoding process.
Receiver: The receiver is the individual or group for whom the message is intended. The receiver’s role is to interpret the message and provide feedback to the sender. Effective communication occurs when the receiver understands the message as the sender intended. The receiver’s feedback helps the sender gauge the effectiveness of the communication and make any necessary adjustments.
Feedback: Feedback is the receiver’s response to the message, indicating whether it was understood correctly. Feedback can be verbal, such as asking questions or providing answers, or non-verbal, such as nodding or facial expressions. Feedback is essential for ensuring that the communication process is complete and that the message has been understood as intended.
- How the Process of Communication Takes Place
The process of communication begins with the sender, who has an idea or information to share. The sender then encodes this idea into a message using words, symbols, or gestures. The message is transmitted through a chosen channel, such as speaking, writing, or visual media. The receiver receives the message and decodes it to understand its meaning. This interpretation depends on the receiver’s knowledge, experience, and context. Once the message is decoded, the receiver provides feedback to the sender, indicating whether the message was understood correctly. Feedback can be verbal or non-verbal, such as nodding, asking questions, or providing answers. This feedback loop helps to ensure that the communication is effective and that any misunderstandings are addressed. Throughout this process, various factors, such as noise, cultural differences, and personal biases, can impact the clarity and effectiveness of communication. Understanding these components and how they interact can help individuals improve their communication skills and ensure that their messages are conveyed accurately and effectively.
Significance of Communication
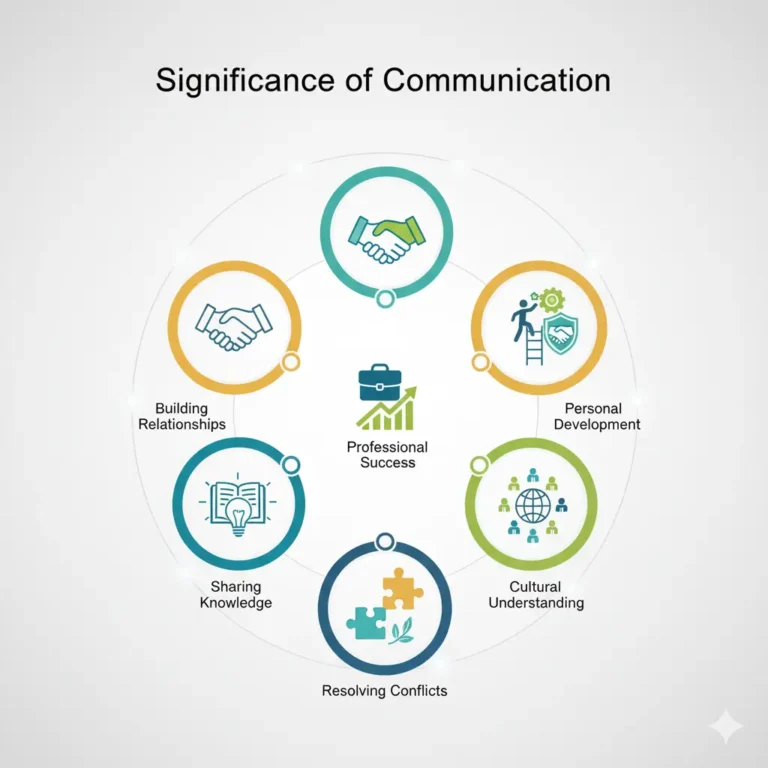
Communication is a key part of our daily lives. It helps us share ideas, information, and feelings with others. Effective communication is important for personal, academic, and professional success. It includes speaking, writing, body language, and visual aids. Understanding the importance of communication can help us build better relationships, share knowledge, and achieve our goals. The following are the major significances of communication:
1. Building Relationships
Communication helps us build and maintain relationships. When we talk openly and honestly with others, we build trust and understanding. In personal relationships, good communication can make us feel closer to friends and family. In professional relationships, clear communication helps teams work better together. It ensures everyone knows their roles and responsibilities.
2. Sharing Knowledge
Sharing knowledge is a major benefit of communication. In schools, teachers use communication to teach students. Clear explanations and interactive discussions help students learn. At work, sharing information accurately and quickly is important. It helps in making decisions and solving problems. Written reports and emails also keep a record of information for future reference.
3. Professional Success
Good communication skills are important for career growth. Being able to explain ideas clearly and persuade others can help in the workplace. Effective communication helps in teamwork and leadership. Leaders who communicate well can inspire and motivate their teams.
4. Resolving Conflicts
Conflicts are a part of life, and communication is key to resolving them. Open dialogue helps people express their views and understand each other. Listening and empathy are important in finding solutions. In both personal and professional settings, resolving conflicts through communication can prevent bigger problems and create a positive environment.
5. Cultural Understanding
In our globalised world, communication helps us understand different cultures. Knowing about different communication styles and values prevents misunderstandings. In international business, understanding cultural preferences can improve negotiations and relationships. Sharing cultural practices through communication promotes inclusivity and enriches our perspectives.
6. Personal Development
Communication benefits in the personal growth. Talking with others helps us understand our thoughts and feelings better. It improves our critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Participating in discussions and public speaking builds confidence and social skills. For example, joining a debate club can enhance speaking abilities and self-assurance.
7. Building Trust
Trust is crucial in any relationship and communication helps build it. When we communicate openly, others feel respected and valued. This strengthens bonds and fosters cooperation. In the workplace, trust built through good communication can lead to more effective teamwork and higher morale.
Types of Communication
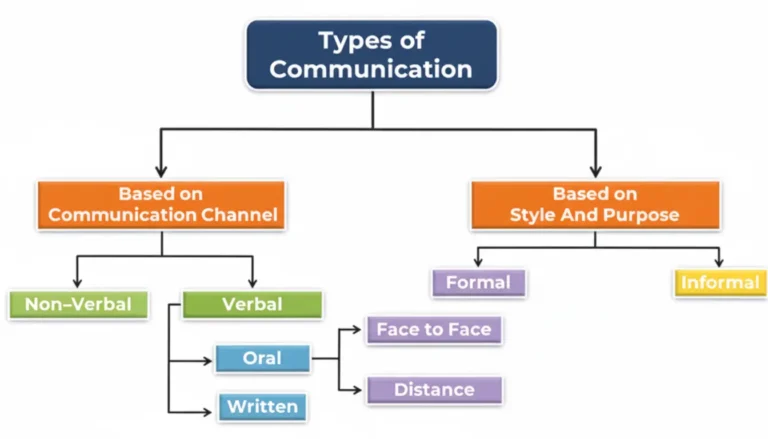
Communication is how we share information, ideas, and feelings with others. It is an important part of our daily lives, whether we are at home, school, or work. Communication can happen in many ways and can be divided into different types. Understanding these types can help us communicate better and more effectively. There are two main ways to classify communication: based on the communication channel and based on the style and purpose.
Based on Communication Channel
1. Non-Verbal Communication
Non-verbal communication is when we use our body to communicate instead of words. This includes facial expressions, gestures, posture, and eye contact. For example, smiling when greeting someone shows friendliness. Non-verbal signs can often tell more than words and are important for understanding the true feelings of a person. It helps convey emotions and attitudes and supports verbal communication by adding emphasis and meaning. For example, nodding while listening shows agreement, and avoiding eye contact might indicate discomfort or dishonesty.
2. Verbal Communication
Verbal communication is when we use words to share information. It can be divided into two types:
a. Oral Communication
Oral communication is speaking with someone face-to-face, on the phone, or through video calls. It allows for immediate feedback and helps in understanding through tone of voice and expression. Examples: Talking to friends, giving a speech, or having a meeting. Oral communication is dynamic and interactive, allowing for adjustments based on the listener’s responses. It also includes listening, which is an essential part of effective communication.
b. Written Communication
Written communication is sharing information through written words. This includes writing letters, emails, texts, and reports. Written communication is useful because it can be saved and referred to later. Examples: Writing an essay, sending a text message, or emailing a colleague. Written communication provides a permanent record of information and is often used for official and formal communication. It requires clarity and precision to ensure the message is understood correctly.
Based on Style and Purpose
1. Formal Communication
Formal communication is used in professional settings or when we need to follow certain rules and etiquette. It is often structured and polite. Formal communication can happen face-to-face or over a distance.
Face to Face: Face-to-face formal communication happens in person, such as in meetings, interviews, or presentations. It allows for direct interaction and immediate feedback. This type of communication is crucial for building professional relationships and ensuring clear understanding. Formal face-to-face interactions are often scheduled and follow an agenda or specific format.
Distance: Distance formal communication happens when people are not in the same place. This includes phone calls, video conferences, letters, and official emails. It is important in business and official contexts where clear and precise information is needed. Distance communication allows for connectivity despite geographical barriers and is essential for global business operations. Formal distance communication often requires careful planning and structured content to convey the message effectively.
2. Informal Communication
Informal communication is more relaxed and casual. It is used with friends, family, and close colleagues. Informal communication is less structured and can happen anywhere, anytime. Examples: Chatting with friends, casual emails, or social media messages. Informal communication helps build personal relationships and create a comfortable environment. It is spontaneous and flexible, allowing for more personal and emotional exchanges. Informal communication can also occur in the workplace, helping to build camaraderie and team spirit among colleagues.
Understanding these types of communication can help us choose the best way to share our messages and understand others better. Whether through words, body language, formal settings, or casual chats, effective communication is key to building strong relationships and achieving success in various areas of life. By recognising the appropriate type of communication for each situation, we can improve our interactions and ensure our messages are clear and understood.
7 Cs of communication

Effective communication is crucial in every aspect of life, whether it is personal, academic, or professional communication. The 7 Cs of communication provide a guideline to ensure that our messages are clear and effective. These principles help us convey our thoughts and ideas accurately and prevent misunderstandings. By following the 7 Cs, we can improve our communication skills and build better relationships. The 7 Cs of communication are: Correct, Complete, Concrete, Concise, Coherent, Courteous, and Clear. They may be explained as follows:
1. Correct: Correct communication means that the information shared is accurate and free from errors. This includes correct grammar, punctuation, and spelling. Ensuring that the information is correct also means that it is factual and reliable. For example, when writing a report, it is important to check the facts and figures to make sure they are accurate. Correct communication helps in building credibility and trust.
2. Complete: Complete communication provides all the necessary information the audience needs to understand the message. It answers all questions the audience might have and includes all relevant details. For example, when giving instructions, make sure to include all the steps required to complete a task. Complete communication ensures that the audience has a full understanding of the message, preventing any confusion.
3. Concrete: Concrete communication means that the message is specific and clear. It uses precise facts and figures, avoiding vague and ambiguous words. For example, instead of saying, “We had a good sales month,” say, “Our sales increased by 20% in June.” Concrete communication makes the message more understandable and convincing.
4. Concise: Concise communication means that the message is brief and to the point. It avoids unnecessary words and repetitions. For example, instead of saying, “Due to the fact that we were late, we missed the bus,” say, “We missed the bus because we were late.” Concise communication saves time and keeps the audience engaged.
5. Coherent: Coherent communication means that the message is logical and well-organised. All points are connected and relevant to the main topic. For example, in a presentation, ensure that each slide flows naturally to the next, and all information supports the main idea. Coherent communication makes it easier for the audience to follow and understand the message.
6. Courteous: Courteous communication means being polite and respectful. It involves considering the audience’s feelings and viewpoints. For example, when giving feedback, use positive language and constructive criticism. Courteous communication helps in building good relationships and promotes positive interaction.
7. Clear: Clear communication means that the message is easy to understand. It uses simple language and avoids jargon. For example, instead of saying, “We need to synergise our operations,” say, “We need to work together more effectively.” Clear communication ensures that the audience grasps the message without any confusion.
By following the 7 Cs of communication, we can ensure that our messages are effective, clear, and well-received by our audience. These principles help us communicate more efficiently and build better understanding in all our interactions.
Barriers to Effective Communication
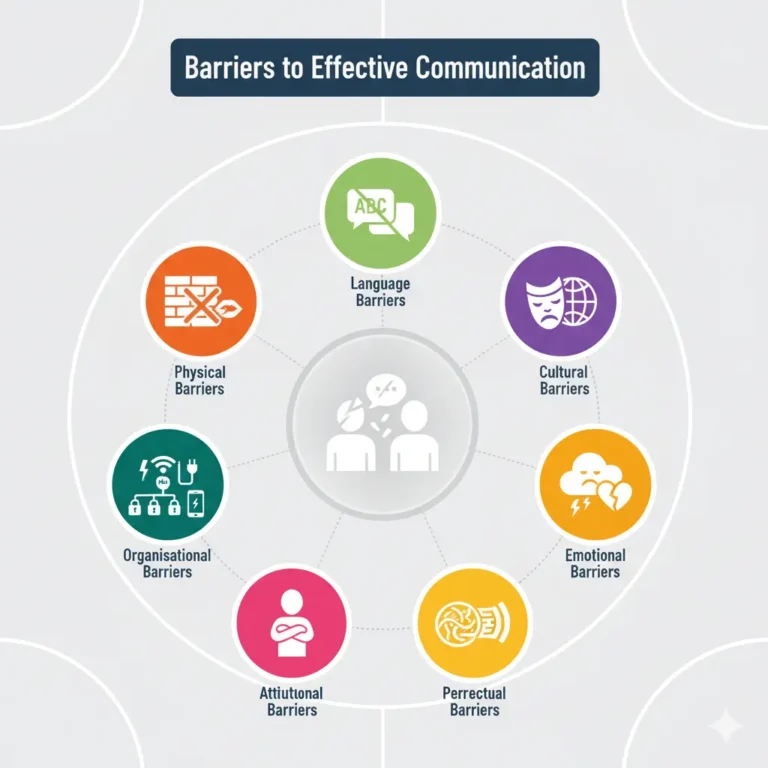
Effective communication is very important in our daily lives. It helps us understand each other and work together. However, communication may not be effective every time because of certain barriers. These barriers can cause misunderstandings and problems. Knowing about these barriers can help us overcome them and communicate better. This content will explain some common barriers to effective communication and how to overcome them.
Physical Barriers
Physical barriers are obstacles in the environment that prevent communication. These include distance, noise, and poor lighting. For example, if you are trying to talk to someone in a noisy room, it can be hard to hear each other. Similarly, if there is a long distance between people, they may not be able to communicate easily.
Language Barriers
Language barriers happen when people do not speak the same language or use different words. This can lead to confusion and misunderstandings. For example, using technical terms with someone who does not understand them can cause problems.
Cultural Barriers
Cultural barriers arise from differences in cultural backgrounds, beliefs, and values. These differences can affect how messages are understood. For instance, a gesture that is friendly in one culture might be rude in another. To overcome cultural barriers, be aware of and respect cultural differences.
Emotional Barriers
Emotional barriers are caused by the feelings of the sender or receiver, such as anger, fear, or stress. These emotions can change the way a message is sent or received. For example, if someone is very angry, they might not listen carefully to what you are saying. To overcome emotional barriers, try to stay calm and patient.
Perceptual Barriers
Perceptual barriers occur when people see things differently because of their past experiences, beliefs, or attitudes. These differences can lead to misunderstandings. For example, if you have had a bad experience with someone, you might not trust what they say.
Organisational Barriers
Organisational barriers are related to the structure and rules of an organisation. These include hierarchical levels, unclear communication channels, and rigid procedures. For example, in a big company, messages can get lost or changed as they go through different levels of management.
Attitudinal Barriers
Attitudinal barriers come from people’s attitudes and behaviours, like prejudice, arrogance, or lack of interest. These attitudes can prevent effective communication. For example, if someone is not interested in what you are saying, they might not listen properly.
Technological Barriers
Technological barriers happen when there are problems with communication tools and technologies. These include poor internet connections, outdated software, or lack of access to technology. For example, a bad internet connection can make video calls difficult. To overcome technological barriers, ensure that your communication tools are up-to-date and working properly. Provide training if necessary so everyone knows how to use the technology.
By understanding these common barriers to effective communication, we can take steps to overcome them. This will help us communicate more clearly and effectively, whether we are talking with friends, family, or colleagues. Good communication is key to building strong relationships and achieving our goals.
Multiple Choice Questions
1. What is the primary purpose of communication?
A) To avoid interactions
B) To share ideas, information, and emotions
C) To create confusion
D) To maintain silence
2. Which of the following is NOT a component of the communication process?
A) Sender
B) Encoding
C) Broadcasting
D) Feedback
3. What does 'encoding' involve in the communication process?
A) Receiving the message
B) Interpreting the message
C) Translating thoughts into a message
D) Providing feedback
4. Which type of communication uses body language instead of words?
A) Verbal Communication
B) Non-Verbal Communication
C) Written Communication
D) Visual Communication
5. What is a common barrier caused by environmental factors?
A) Language
B) Noise
C) Culture
D) Attitude
6. Which barrier to communication arises from different languages or terminologies?
A) Physical
B) Emotional
C) Language
D) Perceptual
7. Which communication type allows for immediate feedback and understanding through tone of voice?
A) Written Communication
B) Non-Verbal Communication
C) Oral Communication
D) Visual Communication
8. Which of the following is an example of written communication?
A) Speaking on the phone
B) Sending an email
C) Gesturing with hands
D) Using facial expressions
9. What does 'complete' communication ensure?
A) The message is brief
B) The message includes all necessary information
C) The message is vague
D) The message is ignored
10. How can emotional barriers be overcome?
A) By ignoring the other person
B) By staying calm and patient
C) By speaking loudly
D) By using complex language
11. What is the role of the receiver in the communication process?
A) To encode the message
B) To send the message
C) To interpret the message and provide feedback
D) To create noise
12. Which barrier is caused by different cultural backgrounds?
A) Technological
B) Organisational
C) Cultural
D) Physical
13. What type of communication is informal and used with friends and family?
A) Formal Communication
B) Written Communication
C) Informal Communication
D) Visual Communication
14. What is a key characteristic of clear communication?
A) Using jargon
B) Being vague
C) Using simple language
D) Being lengthy
15. Which of the following helps in overcoming technological barriers?
A) Ignoring the problem
B) Using outdated tools
C) Ensuring tools are up-to-date and functioning properly
D) Avoiding technology
Assignment Questions
1. Define communication and explain the importance of communication in personal and professional success.
2. Describe the communication process and its components/elements.
3. Define barriers in communication and identify the main barriers to effective communication.
4. Differentiate between verbal and non-verbal communication with examples.
5. Discuss the role and importance of feedback in the communication process.
6. Explain how cultural differences can impact communication with examples.
7. Describe the 7 Cs of communication and explain their importance.
8. Discuss how organisational structure can affect communication.
9. Why is it important to use simple and clear language in communication?
Prepared by Prof. D.C. Nanaware
Edited by Prof. Dr. V.H. Waghmare